About tachograph equipment
How tachographs work and the different types available.
Tachograph recording equipment for trucks over 3.5 tonnes and buses with more than nine seats is mandatory in the European Union (EU). Tachographs record key driver and vehicle information and monitor drivers' compliance with driving time, breaks and rest period rules. They also record vehicle speed, distance travelled and other information.
Recording and reporting of this data helps ensure that drivers are not working beyond agreed safety limits: ensuring they take regular breaks to avoid driving while over-tired and not driving beyond the speed limits for their vehicle and the roads.
Tachograph records must be available for inspection by enforcement officers.

Exemptions from mandatory tachograph laws
Some classes of vehicle are exempt from the EU rules on tachograph and driving times, breaks and rest periods. Drivers who are exempt should still keep a record of their total daily working activity.
Vehicles that are exempt from having to install and use tachographs. Summary of exempt vehicles. Links to detailed exemptions.
Tachograph types
Tachographs come in two types: analogue and digital. The EU introduced analogue tachographs in 1985, while digital tachograph technology replaced the existing analogue recording devices in May 2006.
Goods and passenger vehicles first registered after 1 May 2006 must only be fitted with a digital tachograph. If they are registered before that date, they can be fitted with either type of tachograph.
Tachograph smart cards are part of the digital system, for use by drivers, companies, calibration workshops and enforcement officers.
If a driver is using an analogue tachograph, they are responsible for writing their name, registration number, location of the start and end of the journey and the start and end of the odometer readings on a record sheet every day that they are driving.
Digital tachographs
Digital tachographs became mandatory in new commercial trucks and buses in May 2006.

The provision of tachograph cards for use by drivers, companies, calibration workshops and enforcement officers is central to the operation of digital tachographs.
Data is stored in the vehicle unit memory and on tachograph driver cards. The data contains a range of information including:
- distance covered
- vehicle speed (for previous 24 hours of driving)
- vehicle licence number
- driver activity (driving time, breaks, rest periods, other work, periods of availability).
A driver’s card can store information for a maximum of 28 days before it begins to be overwritten; the vehicle unit has a larger memory capacity and can store data for 365 days.
Analogue tachographs
Analogue tachographs are only fitted to vehicles first registered before May 2006.
The analogue tachograph records:
- speed
- distance travelled
- working activity.
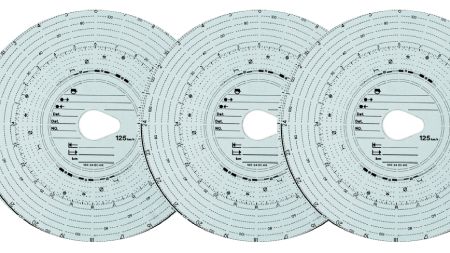
The analogue tachograph chart also contains areas for manual entries of activities such as:
- daily working period
- rest periods
- work done outside of the vehicle.
Vehicle unit (VU)
When a driver takes over a goods or passenger vehicle fitted with a digital tachograph, they must insert the driver card into the digital tachograph unit. Where a vehicle is double-manned, both driver and co-driver must insert their own cards.
Similar to an analogue tachograph, a digital tachograph will record a driver’s activities such as driving, breaks and rest periods. Digital tachographs start recording automatically when the vehicle moves.
Drivers must use the mode switch on the tachograph to record activities including rests, breaks and other periods of availability. The records are stored on both the driver card and vehicle unit. Drivers do not need to manually enter activities recorded on analogue charts onto their driver cards.
Downloading data
A transport operator must download data from the card at least every 28 days and from the vehicle unit at least every 90 days. The data should be kept for inspection by enforcement officers for at least one year from the date of downloading.
To download data from the vehicle unit and driver card, an operator will need a download device and a company card.
Agency drivers
When employing agency drivers, operators are responsible for making sure these drivers return their record sheets. Operators should also download data from the drivers' tachograph cards and retain that data for inspection.
Digital tachograph training
Training in the use of digital tachographs is available for operators and drivers through The Chartered Institute of Logistics and Transport of Ireland. Telephone: (01) 676 3188.
Road Safety Authority (RSA) prosecutions
We are responsible for enforcing EU and national road transport legislation on:
- tachographs
- EU drivers' hours
- Road Transport Working Time Directive elements of the licensing of road haulage and passenger operators to engage in hire and reward operations
- drivers’ CPC.
More information on commercial vehicle legislation.
We initiate prosecutions against drivers and operators who breach the legislation that applies.
Successful prosecutions are published on our website:
RSA prosecutions for breaches of legislation including tachographs, drivers’ hours, drivers CPC. Search for and browse prosecutions. Yearly prosecution totals.